A Gothic Setting
Bram Stoker arrived at Mrs Veazey’s guesthouse at 6 Royal Crescent, Whitby, at the end of July 1890. As the business manager of actor Henry Irving, Stoker had just completed a gruelling theatrical tour of Scotland. It was Irving who recommended Whitby, where he’d once run a circus, as a place to stay. Stoker, having written two novels with characters and settings drawn from his native Ireland, was working on a new story, set in Styria in Austria, with a central character called Count Wampyr.
Stoker had a week on his own to explore before being joined by his wife and baby son. Mrs Veazey liked to clean his room each morning, so he’d stroll from the genteel heights of Royal Crescent down into the town. On the way, he took in the kind of views that had been exciting writers, artists and Romantic-minded visitors for the past century.
The favoured Gothic literature of the period was set in foreign lands full of eerie castles, convents and caves. Whitby’s windswept headland, the dramatic abbey ruins, a church surrounded by swooping bats, and a long association with jet – a semi-precious stone used in mourning jewellery – gave a homegrown taste of such thrilling horrors.
Abbey and church
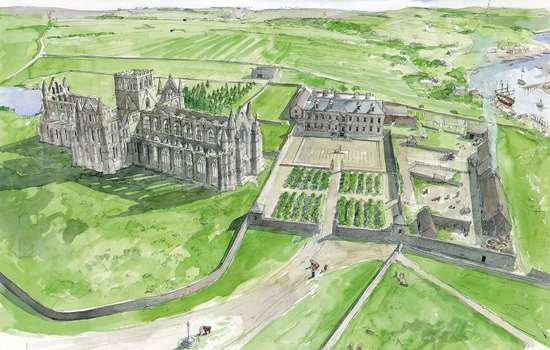
High above Whitby, and dominating the whole town, stands Whitby Abbey, the ruin of a once-great Benedictine monastery, founded in the 11th century. The medieval abbey stands on the site of a much earlier monastery, founded in 657 by an Anglian princess, Hild, who became its first abbess. In Dracula, Stoker has Mina Murray – the young woman whose experiences form the thread of the novel – record in her diary:
Right over the town is the ruin of Whitby Abbey, which was sacked by the Danes … It is a most noble ruin, of immense size, and full of beautiful and romantic bits; there is a legend that a white lady is seen in one of the windows.
Below the abbey stands the ancient parish church of St Mary, perched on East Cliff, which is reached by a climb of 199 steps. Stoker would have seen how time and the weather had gnawed at the graves, some of them teetering precariously on the eroding cliff edge. Some headstones stood over empty graves, marking seafaring occupants whose bodies had been lost on distant voyages. He noted down inscriptions and names for later use, including ‘Swales’, the name he used for Dracula’s first victim in Whitby.
An encounter with Dracula
On 8 August 1890, Stoker walked down to what was known as the Coffee House End of the Quay and entered the public library. It was there that he found a book published in 1820, recording the experiences of a British consul in Bucharest, William Wilkinson, in the principalities of Wallachia and Moldavia (now in Romania).
Wilkinson’s history mentioned a 15th-century prince called Vlad Tepes who was said to have impaled his enemies on wooden stakes. He was known as Dracula – the ‘son of the dragon’. The author had added in a footnote:
Dracula in the Wallachian language means Devil. The Wallachians at that time … used to give this as a surname to any person who rendered himself conspicuous either by courage, cruel actions, or cunning.
Stoker made a note of this name, along with the date.
The birth of a legend
While staying in Whitby, Stoker would have heard of the shipwreck five years earlier of a Russian vessel called the Dmitry, from Narva. This ran aground on Tate Hill Sands below East Cliff, carrying a cargo of silver sand. With a slightly rearranged name, this became the Demeter from Varna that carries Dracula to Whitby with a cargo of silver sand and boxes of earth.
So, although Stoker was to spend six more years on his novel before it was published, researching the landscapes and customs of Transylvania, the name of his villain and some of the novel’s most dramatic scenes were inspired by his holiday in Whitby. The innocent tourists, the picturesque harbour, the abbey ruins, the windswept churchyard and the salty tales he heard from Whitby seafarers – all became ingredients in the novel.
In 1897 Dracula was published. It had an unpromising start as a play called The Undead, in which Stoker hoped Henry Irving would take the lead role. But after a test performance, Irving said he never wanted to see it again. For the character of Dracula, Stoker retained Irving’s aristocratic bearing and histrionic acting style, but he redrafted the play as a novel told in the form of letters, diaries, newspaper cuttings and entries in the ship’s log of the Demeter.
The log charts the gradual disappearance of the entire crew during the journey to Whitby, until only the captain is left, tied to the wheel, as the ship runs aground below East Cliff on 8 August – the date that marked Stoker’s discovery of the name ‘Dracula’ in Whitby library. A ‘large dog’ bounds from the wreck and runs up the 199 steps to the church, and from this moment, things begin to go horribly wrong.
Dracula has arrived …
Find out More
-

Plan your visit to Whitby Abbey
Follow in the footsteps of those like Bram Stoker who have been inspired by the abbey’s soaring Gothic ruins.
-

Literary Links
Throughout the centuries, many of the places that we care for have left their mark on English literature.
-

CÆdmon, Whitby and Early English Poetry
How Cædmon’s poetic awakening at Whitby produced one of the first fragments of English verse.
-
History of Whitby Abbey
Learn more about the history of Whitby Abbey, from its earliest Bronze Age origins to the present day.
